How to connect with 5G (M0090)
Table of contents
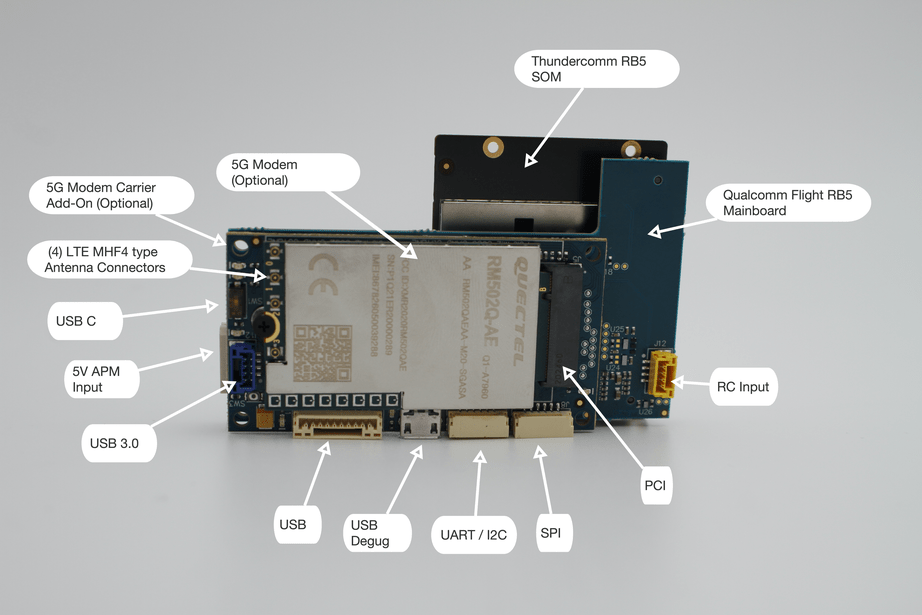
Connecting to 5G network
In order to establish a connection to the 5G network, voxl-modem is required.
Configuring Service
The voxl-modem service can be configured by running the following:
voxl-configure-modem
NOTE: Option “V2” is the Sierra wireless modem board V2 Modem board. Do not select this with a Quectel modem connected
The user will be prompted to select their modem hardware and APN (Access Point Name) for their chosen SIM card.
This will enable the voxl-modem service in the background and it will be started at boot.
Disabling / enabling service
The voxl-modem service can be disabled by running the following:
systemctl disable voxl-modem
The service can be re-enabled by running:
systemctl enable voxl-modem
The status of the service can be viewed by running:
systemctl status -l voxl-modem
Connecting to QGC over 5G
In order to connect QGC over the LTE or 5G network, a VPN will be needed in order to complete the bridge from the cellular network to the drone.
A typical use case of an LTE connection is to connect a drone to a Ground Control Station (GCS) such as QGroundControl. Typically the GCS is also connected to an LTE network. In this case, both the drone and the GCS have been assigned IP addresses on the LTE network that are private to the carrier network. This prevents the drone from directly connecting to the GCS since their IP addresses are not visible to each other over the internet.
There are a variety of ways to solve this issue. ModalAI uses a VPN as the preferred solution.
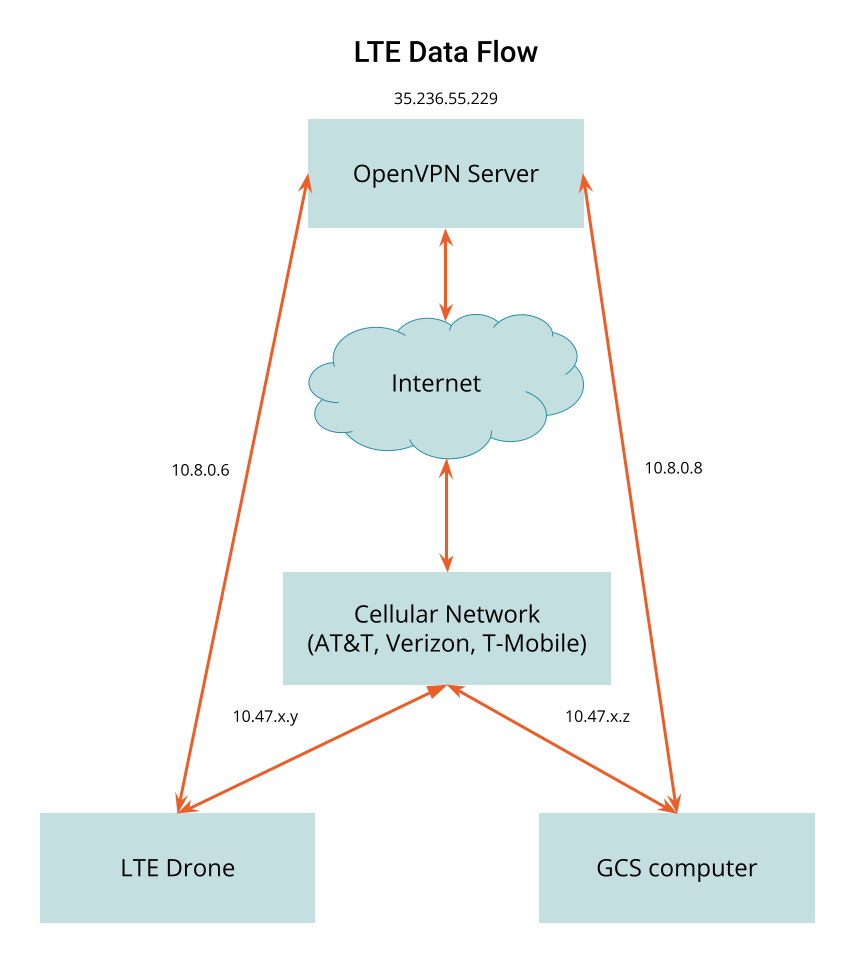
This diagram shows how the VPN solution works. In this example a server is allocated with a static IP address, 35.236.55.229. For QRB5165 based devices, we prefer to use Tailscale as our VPN provider.
If you prefer to host your own server, you can do so with Google Cloud Platform, Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, etc. Ubuntu is our preferred OS for our servers. Our self-hosted VPN server is setup using the OpenVPN software package.
In the example above, once the drone has connected to the AT&T network, it obtains the IP address 10.47.x.y and the GCS, once connected, obtains the address 10.47.x.z.
With the VPN server software running on the cloud server and VPN client software on both the drone and the GCS, the devices can now connect and get VPN IP address assignments. In this diagram, the drone is assigned 10.8.0.6 and the GCS is assigned 10.8.0.8. The drone can now communicate directly to the GCS using the 10.8.0.8 IP address.
It is desirable for the drone and the GCS to always get the same IP address when connecting to the VPN. This is possible by assigning each separate network endpoint a unique security certificate. When each endpoint connects using it’s certificate it can be configured to receive the same address every time.